WHAT IS HAND INFECTION?
Hand infections are the microbic diseases that may be fatal if not treated properly. In most of these diseases, duly performed wound care and oral antibiotic treatment is sufficient. In same rarely seen deep hand infections, there is a risk of necrosis (necrotizing infections) and the spread of bacteria to the body (bacteremia and sepsis). In the follow-up of these cases, regular surgical debridement (clearing of the necrosis), drainage, intensivecare unit conditions and/or amputation might be required (figure 1).
[auto_thumb width=”270″ height=”150″ link=”https://www.hakangundes.com.tr/wp-content/uploads/1h1.jpg” lightbox=”true” align=”center” title=”” alt=”” iframe=”false” frame=”true” crop=”true”]https://www.hakangundes.com.tr/wp-content/uploads/1h1.jpg[/auto_thumb]
HOW DOES IT OCCUR?
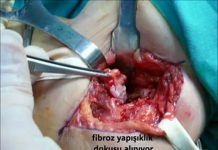
Hand is the organ with the highest risk of being injured as required by its function. Any kind of sharp or blund injuries may cause to the infection on the hands. Most of the occuring infections are the superficial infections through which the cutaneous and subcutaneous tissue is effected. However, since the skin, tendon, bone and the joint is so close to each other in our hands, the infections should be closely followed-up. Uncontrolling of the infection may result in the loss of the function of the hand or amputation (figure 2 and 3).
In the development of the infection; the factors of the patient (host) and the bacterias are also as important as the features of the hand. For example, while the trauma and the hit starts the wound on the hand, the patient’s having diabetes will easen the development of the infection. Likewise, in the process of long term diseases like dermatitis may cause to the infections. Increasing resistance of some bacterias within the society to the medicine has caused to the development of the bacterias and changed the treatment. Even in the Standard treatment regimes (outpatients taking antibiotics) the controls should be made on the third and the seventh day so as to early detect the non-respond to the treatment and the possible complications.
Paronychia
Paronychia is the infection of the skin covering the nail. Pain, swelling and rushes are observed on the nail root. Trauma, manicure, frequently washing the dishes and ingrown nail are the main reasons. The factor is most commonly the gram positive bacterias. If there is no abcess, warm bath and oral antibiotic treatment will be sufficient. In case of abcess, the laceration and the abcess should be discharged. In the chronic cases, fungal infections should be suspected.
FELON
Felon is the abcess developing on the fingertips suddenyl started and throbbing severe pain, rushes and edema can be accompanied by the necrosis (figure 4). The infection may spread to the bone (osteomyelitis). Felon is generally starts upon a perforating trauma, thus the most commonyl effected fingers are the thumb and the forefinger. Extension of the paronychia to the finger bed may cause to the felon, too. In case the abcess does not automatically discharges, drainage is required. Keeping the hand high, taking oral antibiotics and warm bath two times a day are recommended. Radiological examination should be performed in order to eliminate the bone infection. The surgical intervention of the abcessed paronychia, felon and all hand infections should be carefully performed by the specialist.
[auto_thumb width=”270″ height=”150″ link=”https://www.hakangundes.com.tr/wp-content/uploads/3h1.jpg” lightbox=”true” align=”center” title=”” alt=”” iframe=”false” frame=”true” crop=”true”]https://www.hakangundes.com.tr/wp-content/uploads/3h1.jpg[/auto_thumb]
In accordance with the stage of the superficial infections of the hand, penicilin G procain, ampisilin-sulbactam tb, oral or parenteral cephalosporin, clindamisin, trimethoprim/ sulfamethoxazole can be safely used.
The agents that can be topically used are bacitracin, neomicin, polymyxin cream, gentamicin cream and mupirocin cream.
HERPETIC WHITLOW
Herpetic whitlow is the most commonly seen viral infection. It generally develops with type 1 or type 2 virus settlement on the damaged skin. The The healtcare workers subjected to mouth secretion are under risk (especially they are abiding by the contact warnings). The clinical findings are suddenyl started edema, rush and local pain. They can be accompanied by the fever, elbow and axillary lymph node swelling. The vesicles combine in time and may seem like abcess. If the herpetic whitlow develops on the fingertip, it might be comfused with paronychia or felon. Generally, it is expected to automatically heal within the first two-three weeks. If acyclovir, famciclovir or valacyclovir is started within the fisrt 48 hours following the occurence of the lesion, the severeness and the term of the infection may be shotrhened. Since the vesicule liquid includes virus, it should be closed with a dry scloth in otder to prevent the spread. Since the surgical interventions to be performed on the lesion will increase the viremia and bacterial infection risk, it is not recommended. 30-50% of the cases can be repeated; if the infection occurs three or more than three times a year, long term supressing treatment can be preferred.
PYOGENİC FLEXOR TENOSYNOVİTİS
Tendons are the edges of the muscles in our arms. In other words, they are the rope-like tissues penabling the muscles to stick on the bones and convey the power. We can consider the tendons like the ropes conveying the muscle strenght to the bones to provide the finger movements. The after the tendons reach to the fingers, they move within the surrounding sheath. Tendon moves within this sheath like a train passing through a tunnel. This sheath is called synovia. Pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis is the name given to the bacterial infection of the tendon and the surrounding sheath. It requires early surgerical intervention due to the risk of spreading up to the arm through the tunnel. This disease reveals itself with four clinical findings (figure 5):
[auto_thumb width=”270″ height=”150″ link=”https://www.hakangundes.com.tr/wp-content/uploads/4h1.jpg” lightbox=”true” align=”center” title=”” alt=”” iframe=”false” frame=”true” crop=”true”]https://www.hakangundes.com.tr/wp-content/uploads/4h1.jpg[/auto_thumb]
1) symmetrical (equal in both sides) swelling is observed on the finger
2) The finger is relaxed and painless in flexion.
3) There is spread sensitivity in the palmar side of the finger.
4) Passive extansion of the finger is painful.
Although it occurs upon a trauma or drilling injuries, it might also occur upon spread of some pathogens thhrough blood. (like Neisseria gonorrhea ). Early diagnosis is important to prevent tendon death, adhesions and the spread of the infection to the deep tissues.
TREATMENT
It is important to abide by 3 main principles in the approach of such infections:
1-Giving the appropriate antibiotic at appropriate dose in the control of the infection (especially in the existence of local spread, lymphangitis and septicemia).
2-Performing the surgical intervention to discharge inflammation and clear the necrosis with minimum tissue damage.
3-Keeping the hand high with a splint as long as the infection continues.
In the very early period, splint, keeping the hand high and iv antibiotic treatment will be sufficient. It is possible to determine the stage and limits of the infection and eliminate the abcess with US. The appropriate antibiotic treatment should be directed to gram positive bacterias. In the existence of the diabetes and other immune suppresive conditions, it has be accepted that the infection is composed of more than one bacteria (polymicrobial). The antibiotic to be started in this stage should also be effective on the bacterias called anaerobe. If the antibiotic treatment does not respond within 72 hours, surgical intervention should be preferred. Since the tissue spread and spread through blood risk is high in the immune suprpressed patients, the decision for surgical intervention can be taken earlier. The antibiotic treatment should be completed in 12 to 21 days.
BITE INFECTIONS
The infections occuring after the human or animal bites and punch are typically observed on the dorsum of the hand (figure 6). Following a 3-5 mm skin injury, the bacteria originating from the mouth or skin flora create infection. It is stated that 1% of the emergency service applications are upon the bites. Generally, it is observed that one of each five bites has infection. With the imaging methods, it should be shown that there is no fracture, foreign object, gas, abcess or osteomyelitis on the infection surface. In the existence of such infections, the wound should be cleaned by debriding with normal saline and samples should be taken form the deep tissue. The wound should be sutured and closed and left to heal automatically (figure 6). The hand should be taken to rest with a splint after the dressing and kept high. In the early treatment of these infections, oral antibiotics can be used. However, in case of any of the following situations, the patient should be hospitalized and iv treatment should be started:
[auto_thumb width=”270″ height=”150″ link=”https://www.hakangundes.com.tr/wp-content/uploads/5h1.jpg” lightbox=”true” align=”center” title=”” alt=”” iframe=”false” frame=”true” crop=”true”]https://www.hakangundes.com.tr/wp-content/uploads/5h1.jpg[/auto_thumb]
1) diabetes or occlusive vein disease,
2) Suppressed immune system (medication, disease etc.)
3) Wound existing more than 24 hours,
4) Joint capsule or bone injury,
5) Patient noncompatible with the treatment,
6) Systemic findings (fever, leucocyte increase etc.
7) Cellulitis (soft tissue infection)
The treatment should be continued for three weeks in the tenosynovitis diagnosis and 6 weeks in the osteomyelitis diagnosis.
In each bite cases, tetanus immuneglobin and tetanus toxoid, and in the cases without the existence of vaccinaction card, hydrophobia prophylaxis is recommended.
CELLULITIS AND ERYSİPELAS
It is the condition when the bacterias reach to the subcutaneous through the acesses caused by some skin diseases like scar, laceration or eczema and result in infection. The acsesses can also be the vascuolar accesses on the dorsum of the hand. While sellulitis is more commonly seen on the middle aged and old population, erysipelas is commonly seen on the pediatric or old population.
SYMPTOMS
Cellulitis and erysipelas revelas itself with rush, edema, temperature increase and sensitivity without any underlying focus point (figure 7). In the erysipelas, the wound is seperated from the healthy skin with a significant line and has orange peel appearance. Erysipelas is a more acute condition when compared to the cellulitis. However, cellulitis is a more insidious infection with clinical findings progressing in days. Both infections are most commonly seen on the legs, rarely on the arms, eyes, h Selülit ve ead and neck.
[auto_thumb width=”270″ height=”150″ link=”https://www.hakangundes.com.tr/wp-content/uploads/6h1.jpg” lightbox=”true” align=”center” title=”” alt=”” iframe=”false” frame=”true” crop=”true”]https://www.hakangundes.com.tr/wp-content/uploads/6h1.jpg[/auto_thumb]
HOW TO DIAGNOSE?
The diagnose is mainly established with clinical appearance. Blood cultures, needle aspiration and punch biopsy samples are generally not helpful. Blood culture positivenss is less than 5%. The possility of having bacteria from biopsy sample is 20-30%. The samples from the wound surface cannot be accepted due to the risk of contamination. Radiological examination should be made in order to eliminate the necrotizing fasciitis (abcess, gas and osteomyelitis).
WHAT IS THE TREATMENT?
Empirical antibiotic treatment should be directed to β- hemolytic streptococcus and S. Aureus. The treatment should include MRSA fort he patients with repeated infections, underlying diseases and previously had MRSA development. In case the factor is MRSA, teicoplanin and linezolid, in case of polymicrobial tigesiclin can be used. The teeatment should be completed on the 7th-12th day.
NECROTİZİNG INFECTIONS
DEFINITION
The soft tissue infections that are rapidly advancing, causing to sudden necrosis and life threatining by spreading thrtough blood are called as necrotizing infections (NF). It is known with high mortality risk. Since the tissue damage is quick and deep, early surgery is life saving.
WHAT IS THE CAUSE?
There are some issues indicating that 85% of the cases are caccompanied by a chronic disease. Diabetes, high blood pressure, vascular insufficiency, obesity, alcohol/drug addiction, immune supressive treatment and HIV infection are the main risks for NF. Among these diseases, diabetes is the most commonly seen (57%) chronic disease. Skin scars occurring on the soil and surgical lacerations may be the Access holes of the bacterias.
HOW TO DIAGNOSE?
As world-wide known, one of the most important infection urgencies, necrotisin fasciitis (NF) is the sepsis condition when bubbles occur subcutaneously (crepitation) and edema, bulla and necrosis revelas.the first symptom is generally deep tissue pain non-responding to the analgesic. As the disease advances, it is accompanied by the skin and fascial necrosis, bulla and loss of motion (figure 8 and 9).
The imaging methods used for establihing a diagnosis are direct x-ray, magnetic resonance examination (MRI) and computerised tomography (CT). In all of these examinations, the existence of air in the muscles is searched. Blood culture pıositiveness is between 20-60%.
Even in the case of positive blood culture, many other types of bacterias can be the factors on the soft tissue. Culture can be cultivated with bulla liquid and tissue aspiratoin but they are not as meaningful as deep tissue cultures.
SURGICAL DIAGNOSE AND TREATMENT
Necrotisin fasciitis diagnose is establihed surgically. A scoring system defined in 2004 (LRINEC) is used to establih a diagnose.
The treatment of the necrotising soft tissue infections is started with urgently opened laceration and surgical debridement. Together with the surgical cleaning, antibiotic treatment and hemodynamic support should be started. Imaging methods are important to support the diagnosis; however being negative does not eliminate the diagnosis.
WHAT IS THE PROGRESS OF SURGICAL TREATMENT, WHAT IS AHEAD OF US?
In the necrotising infections of the hand, surgical intervention is life saving. Debridement should be performed daily until the end of the necrosis. Another diagnosing approach is to examine the deep tissues (fascia) with the gloved fore finger (finger test) through a 2 cm laceration under local anesthesia. The test is considered as positive if there is no bledding, smelly inflammation and loss of resistance in the tissue. Surgical diagnosis is establihed if the opened soft tissue is dustry gray, the discharge is smelly and there is no bleeding.
HYPERBARİC OXYGEN THERAPY
Hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) is a systemic treatment method that the patients are breathing 100% oxygen while under increased athmospheric pressure up to 3 (ATA), above the normal athmosphere pressure (1 ATA= 760 mm mercury). In accordance with the condition of the patient and the protocol performed, the following benefits are expexted with a HBO treatment performed once or two times a day:
1) Blood and oxygen density increases. Under the tissue oxygen pressure increasing as a result, the toxin production of the bacteria is suppressed and bacteriostasis develops.
2) the tissue subjected to the infection has low oxygen density due to the edema and perfusion decrease. The tissue oxygen level increases with HBO treatment and white blood cell functions are recovered. Besides, with the production of collagen supporting the capillary increase, fibroblast division is increased. In this way, the occurence of capillary rich bed on the open amputation stumb subjected to the infection or grafted bone or tissue is accelerated. With this enrichment and tissue oxygen density increase, the healing speed is expected to be higher on the local perfusion insufficiency, infected ulcer chronic osteomyelitis, compartment syndrome and communitive infected fracture.
3) as there will be icrease in the phagocytose capacity of the leucocytes which are not fully functional in the hypoxic and infected tissue, there will also be increase in the speed of the phagocyte in exterminating the bacterias they involve.
4) It increases the efficiency of the antibiotics like vancomisin, siprofloxacin which have less efficiency in hypoxic environment
In the HBO treated patients, it has been observed that the speed of healing of the wound is meaningfully shothrned to 28 days (when compared to 48 days) following the first debridement.