KIENBÖCK’S DISEASE
WHAT IS KIENBÖCK’S DISEASE?
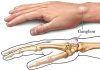
8 small bones unite like clock gears and compose the wrist joint. This condition makes our wrist to be more movable than other joints (figure 1). One of the most important of these 8 bones composing the wrist is the semilunar shaped bone which is called “Lunatum” in Latin. The wrist movements mostly occur between these two wrist bones called Lunatum and Scaphoid (figure 2).
Kienböck’s disease is the condition when the blood stream of the bone called Lunatum decreases or ends (figure 3). Even though many theories have been set forth, the exact reson of the disease is not found out yet. Repeated trauma (hittingi strainingi forcing etc.) may effect the blood stream. But for now, Kienböck’s disease is not associated with any occupatioanl group or usage position.
Besides, the most important assumption regarding the reason of the disease is the structional (anatomical) disorders:
1( There may be some chagnes in the arterial or vein systems of the bone called Lunatum and this may effect the blood stream of the bone.
2)The Lunatum bone may be congenitally different and this may effect the blood stream of the bone.
3) Another and the most important observation is that one of the forearm bones (Ulna bone) of the patients diagnosed with Kienböck’s disease is shorter than the other one (figure 4).This shorthness may effect the blood stream by crushing (nutcracker) the Lunatum bone. The shortness is in milimetric sizes and can onyl be detected in the x-ray graphies. It cannot be detected with outer observation or examination.
HOW TO DIAGNOSE?
The most important symptom is the pain. It starts insidiously and increase within weeks and months. The pain felt while resting is an important finding. The pain is felt on the dorsum and middle side of the wrist joint. The diagnosis of Kienböck’s Disease is established by physical examination and x-rays. Generally, MR examination is required for diagnosis and the treatment plan (figure 5).
[auto_thumb width=”370″ height=”320″ link=”https://www.hakangundes.com.tr/wp-content/uploads/5c1.jpg” lightbox=”true” align=”center” title=”” alt=”” iframe=”false” frame=”true” crop=”true”]https://www.hakangundes.com.tr/wp-content/uploads/5c1.jpg[/auto_thumb]
(Figure 5)
WHAT IS THE PROGRESS OF THE DISEASE?
The disease is divided into four groups in accordance with the radiological examinations. It is difficult to propose whether the disease will progress or if progress how much it will effect the patient if not treated. The relevant studies show us that the disease is generally progressive and limiting (figure 6 and 7). There is no medical (with medication) treatment fort his disease. It has been observed that some implementations like splint, plaster or physical therapy have not changed the progress of the disease but have decreased the pain and the limitation. Mostly, Lunatum with no blood stream reacts like decay (osteonecrosis). Accordingly, bone collapse or crush starts. After this stage, the biomechanic of the whole wrist changes, and cartilage abrasion (arthritis) occurs due to the abnormal load and pressure on the other joints.
WHAT IS THE TREATMENT?
Surgical treatment is the only option to prevent to progress of the disease. Surgical options vary in accordance with the stage of the disease.
In the early stages, the difference between the forearm bones is made up (the longer radius is shortened) and by decreasing the pressure on Lunatum, the collapse is prevented (figure 8 and 9). One of the most significant advantages of this method is that no joint stiffness is observed after the surgery as no intervention is performed to the wrist joint. In some cases, even the patient has Kienbökc’s Disease, his forearm bone (ulna) is not shorter. Thus, with a different surgical method, the small bones on the wrist joint are fixed and the pressure is decreased (figure 10). there will be joint stiffness aftwer the surgery as an intervention is performed to the wrist joint (limitation of movement is observed). This limitation is generally permanent and it is difficult to propose the amouunt of dysmotility to be encountered. The pain is relieved after both surgeries. Another method is the intervention to provide the blood streeam to the bone again.
In the advanced stages, the only surgeries to be performed are the removal of some of the wrist joint bones (proximal line carpectomy) or fixation the wrist joint as a whole (arthrodesis) (figure 11 and 12). In the first option, the amount of permanent dysmotility on the wrist joint after the surgery is low and the pain is relieved in time. Besides, a more strengthless hand and wrist is acquired. In the second option, while there is no loss of strenght after the surgery, all the hand movements are sacrified. In the selection of the surgical method, the preference, occupation, needs and daily life activites of the patient should be taken into consideration as much as the stage of the disease.
WHAT IS THE PROGRESS OF SURGICAL TREATMENT, WHAT IS AHEAD OF US?
After your consultation with the Orthopedician or Hand Surgeon, X-Rays and MR examinations shall be performed. Even rarely, bone scintigraphy or CT (computerized tomography) may be required. What is aimed here is the determination of not only the diagnosis but also the stage of the disease. The stage of the disease has great importance on the selection of the operation to be performed. Your condtions are also equally important. The effect of your right or left hand, your occupation and expectations are also to be taken into consideration. In most of the surgical methods, one day of hospitalization shall be enough. During your consultation with the anesthiologist, you should mention about your special conditions (chronic diseases, regularly taken medicatio etc.). Most of the surgical operations regarding the Kienböck’s Disease are performed under local anesthesia. In the early postop period (first 3 to 5 days), cold application and keeping your hand above the heart level will relieve the pain and throbbing. After the operations, mostly a plaster or a splint extending to the elbow joint is applied. The period of the splint or the plaster may change from 3 weeks to 3 months as required by the surgical method performed. After this period, physical therapy and rehabiltation starts. The aim here iis to gain the strenght of hand, wqrist and the arm and to minimize the loss of motion. The period may change in accordance with the performed surgical operation and the condition of your wrist.
PROBABLE COMPLICATIONS
The most common complications are hematoma on the surgically operated area, infection, compression and pressure feeling due to the plaster, limitation of finger movements due to the tissue adhesion on the surgically operated area, chronic pain (RSD), gettin late or never getting the expected results.
It should not be forgotten that the Kienböck treatment is a hard and long term to take months. In some cases, if the progress of the disease is not prevented, another surgical intervention may be required.
Prof.Dr.Hakan Gündeş’in yayınlarına ulaşmak için lütfen aşağıdaki linklere tıklayınız